Summary Points
-
Innovative Monitoring: Researchers developed a non-invasive system combining optoacoustic detection and terahertz spectroscopy to accurately monitor blood sodium levels, crucial for managing dehydration, kidney disease, and various disorders.
-
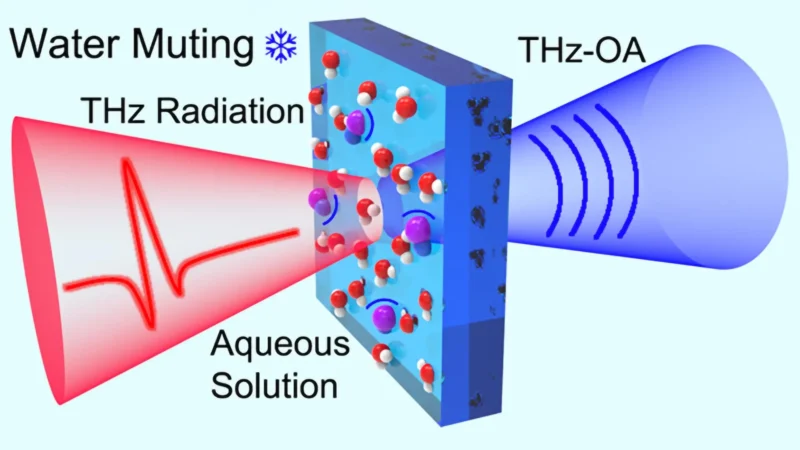
Terahertz Advantages: Terahertz radiation effectively penetrates biological tissues, is non-harmful, and offers low-energy detection sensitive to biological changes, though traditional challenges included interference from water and detecting non-water molecules.
-
Promising Results: The new system demonstrated the ability to measure sodium levels in living mice and human volunteers, effectively distinguishing sodium concentrations without the need for blood draws, paving the way for real-time health monitoring.
- Future Applications: This technology could extend beyond sodium detection to identifying various biomolecules in the body, with ongoing efforts focused on improving signal detection and minimizing water interference for practical clinical use.
The Future of Blood Monitoring
Innovative technology promises to transform how we monitor blood sodium levels without needles. Recent research introduces a system that utilizes optoacoustic detection alongside terahertz spectroscopy. This combination enables accurate, continuous monitoring of vital sodium levels, crucial for managing conditions like dehydration and kidney disease. Traditional blood tests are invasive and often uncomfortable. In contrast, this new approach focuses on non-invasive methods, reducing patient stress and risks associated with blood draws.
Terahertz radiation serves as a low-energy form of energy that poses no harm to body tissues. This aspect makes it ideal for medical applications, as it minimizes risks during monitoring. Researchers overcame significant challenges in detecting sodium ions in complex biological samples using this technology. As a result, they demonstrated successful in vivo detection of sodium levels in live mice. Preliminary trials on human volunteers also showed promising results. Such advancements could pave the way for real-time monitoring of sodium levels, essential for critical patient management.
From Lab to Life
The implications of this technology reach far beyond sodium detection alone. By recognizing unique terahertz absorption signatures, the system may identify various biomolecules, which could enhance our understanding of multiple health conditions. Researchers aim to refine their methods, seeking optimal detection sites on the human body that allow quick measurements while minimizing water interference.
The practicality of widespread adoption hinges on overcoming current limitations. Finding viable body areas for monitoring will be crucial, as will developing techniques that enhance signal clarity without relying on cooling. With that said, the promise of non-invasive monitoring can lead to safer, more effective patient care. This innovation could reshape our approach to health monitoring. In a world where technology increasingly interfaces with healthcare, such advancements underscore significant potential in enhancing human well-being.
Stay Ahead with the Latest Tech Trends
Explore the future of technology with our detailed insights on Artificial Intelligence.
Explore past and present digital transformations on the Internet Archive.
TechV1