Top Highlights
-
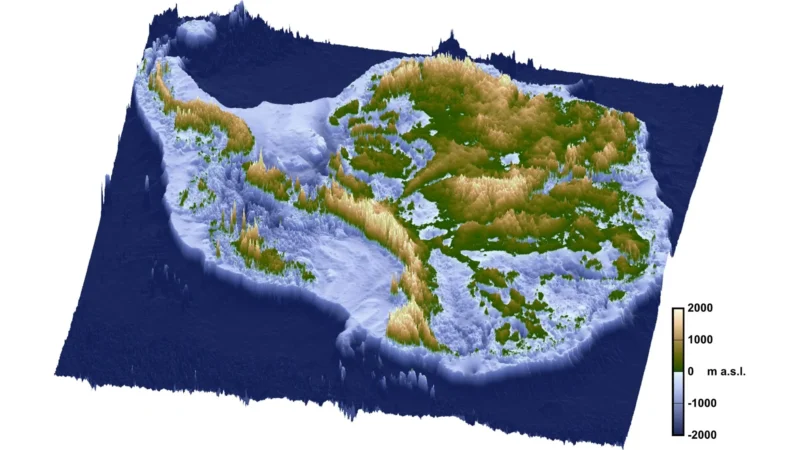
Discovery of Ancient Landscapes: Researchers have uncovered extensive, previously unmapped flat surfaces beneath East Antarctica’s ice, believed to be formed by ancient rivers when East Antarctica and Australia separated 80 million years ago.
-
Barrier to Ice Flow: These flat surfaces, now buried under ice and separated by deep troughs, currently act as barriers that regulate the flow of ice, potentially impacting the rate of ice loss from the region.
-
Impact on Sea Level Projections: The findings could enhance predictions regarding the East Antarctic Ice Sheet’s response to climate change, with the potential for a complete melt raising global sea levels by 52 meters (170 feet).
- Future Research Directions: The study highlights the necessity for further exploration, including drilling to understand the geological history of these surfaces and their influence on ice movement during warmer climate periods.
Uncovering Hidden Landscapes
Recent discoveries beneath East Antarctica’s ice sheet offer exciting insights into our planet’s climate future. Researchers used radar technology to uncover extensive flat surfaces buried under ice. These features, formed by ancient rivers around 80 million years ago, now lie hidden, separated by deep troughs that guide glaciers. Interestingly, the ice flowing over these surfaces moves much slower compared to other regions. This slow movement suggests that the ancient landscape functions as a barrier, potentially regulating the rate of ice loss, a critical factor as global sea levels rise.
Understanding these landscapes helps refine predictions about the East Antarctic Ice Sheet’s response to climate change. This ice sheet holds the potential to raise global sea levels by an alarming 170 feet if it were to melt completely. By incorporating these newly mapped features into predictive models, experts can better gauge how this region may affect global sea levels under various warming scenarios. These advancements represent a vital step in protecting coastal communities worldwide.
Implications for Our Future
The implications of this research stretch far beyond scientific curiosity. They illustrate how our understanding of ancient landscapes can inform present-day climate models. The preservation of these surfaces over millions of years indicates a key aspect of Earth’s climatic history: the ice sheet’s complex interplay with the landscape below. As researchers plan to drill through the ice to retrieve rock samples, they can gain crucial data about past climates. Analyzing these samples will enhance predictions about how the ice may behave in a warming world.
Furthermore, these findings emphasize the need for continued exploration and collaboration. Interdisciplinary efforts bring together expertise from various institutions globally. The insights gained from this research could influence climate policy and resource management. Ultimately, as we strive to navigate the challenges of climate change, understanding the forces at play beneath the ice can lead to more informed decisions for future generations.
Discover More Technology Insights
Explore the future of technology with our detailed insights on Artificial Intelligence.
Access comprehensive resources on technology by visiting Wikipedia.
TechV1