Summary Points
-
Breakthrough in Cooling: Researchers at EPFL have developed a device that operates efficiently at millikelvin temperatures, essential for quantum computations, overcoming the heat dissipation challenge faced by current technologies.
-
Innovative Material Combination: The device utilizes a novel combination of graphene and indium selenide, leveraging their unique properties to achieve high performance in thermoelectric conversion at ultra-low temperatures.
-
Maximizing the Nernst Effect: By harnessing the Nernst effect, this two-dimensional device generates electrical voltage under varying temperatures and magnetic fields, enhancing energy conversion efficiency critical for quantum systems.
- Implications for Quantum Technologies: The findings indicate a significant advancement in nanotechnology, potentially revolutionizing cooling systems essential for scalable and effective quantum computing applications.
A Breakthrough in Quantum Cooling Technology
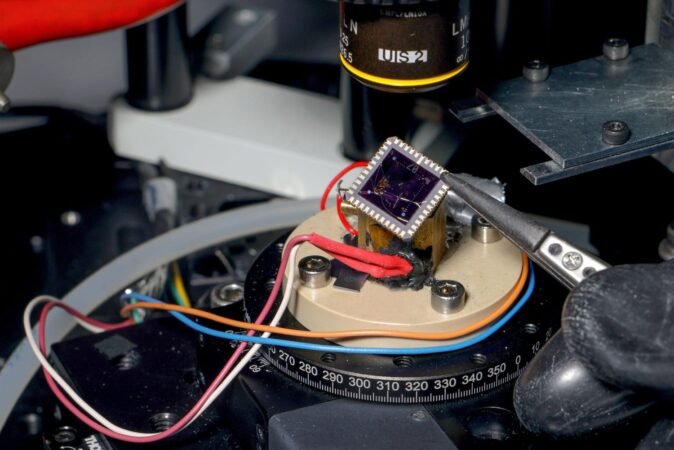
A team of researchers at EPFL’s Laboratory of Nanoscale Electronics and Structures (LANES) has made significant strides in quantum computing. They developed a two-dimensional (2D) device that efficiently keeps quantum computers cool. This innovation addresses a critical challenge in the field.
To perform quantum computations, qubits must remain extremely cold, near -273 degrees Celsius. This temperature minimizes atomic motion and reduces noise. However, the electronics required to manage quantum circuits produce heat, complicating temperature control. Most existing technologies separate quantum circuits from their electronics, leading to inefficiency and noise.
Andras Kis, the project leader, emphasized the importance of this new device. “We are the first to create a device that matches the conversion efficiency of current technologies but operates at low magnetic fields and ultra-low temperatures,” said Gabriele Pasquale, a PhD student in the lab. He described the breakthrough as a step forward in quantum technology.
This innovative device combines graphene, known for its excellent electrical conductivity, with the semiconductor properties of indium selenide. Its 2D nature allows for superior performance and efficiency. The team utilized the Nernst effect, which generates electrical voltage in response to temperature variations in a magnetic field. The unique structure enables precise manipulation of this effect through electrical means.
Additionally, the device relies on a specialized dilution refrigerator that reaches astonishingly low temperatures of 100 millikelvin—colder than outer space. By harnessing the Nernst effect, it overcomes significant obstacles related to heat conversion at these low levels, filling a crucial gap in quantum technology.
Pasquale pointed out the challenges faced by quantum computing systems today. "In quantum systems, there is currently no mechanism to prevent heat from disturbing the qubits. Our device could provide this necessary cooling." His research highlights the mostly unexplored area of thermopower conversion at low temperatures and its potential impact on future technologies.
With promising high conversion efficiency and manufacturable electronic components, the LANES team envisions their device being integrated into existing low-temperature quantum circuits. “These findings represent a major advancement in nanotechnology and hold promise for developing advanced cooling technologies essential for quantum computing,” Pasquale stated. This breakthrough could revolutionize how the industry handles cooling systems for future quantum technologies.
Discover More Technology Insights
Dive deeper into the world of Cryptocurrency and its impact on global finance.
Explore past and present digital transformations on the Internet Archive.
QuantumV1
https://www.techexplorist.com/2d-device-keep-quantum-computers-cool/85984/#utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=2d-device-keep-quantum-computers-cool