Quick Takeaways
-
Ion Channels and Nanotechnology: Ion channels are crucial for biological functions, controlling the movement of charged particles. Their reproduction at subnanometer dimensions poses significant challenges in nanotechnology.
-
Innovative Research: Researchers at The University of Osaka developed a miniature electrochemical reactor that creates pores nearing subnanometer sizes, mimicking natural ion channels’ behavior.
-
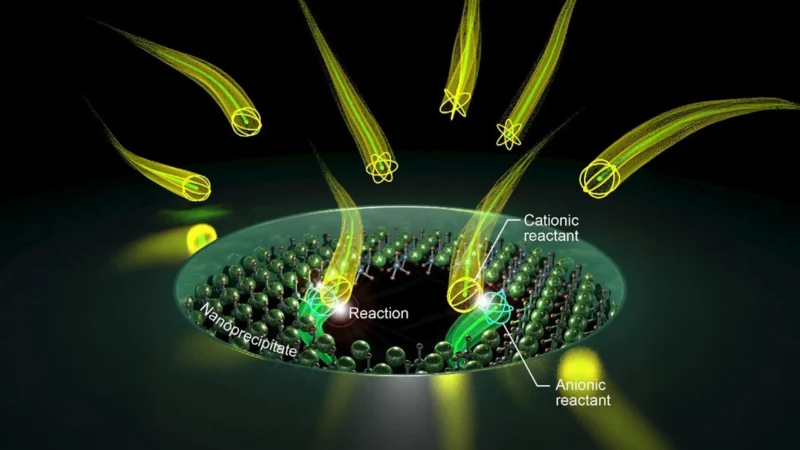
Controlled Pore Dynamics: The team demonstrated the capability to repeatedly open and close these pores through electrical signaling, effectively controlling ion flow and size via chemical adjustments.
-
Potential Applications: This technology can advance fields like DNA sequencing, neuromorphic computing, and nanoreactors, enabling sophisticated studies of ion movement and interactions in confined spaces.
Mimicking Nature’s Precision
Recent research highlights a breakthrough in nanotechnology that could greatly enhance our understanding of biological processes. Scientists have successfully replicated ion channels, which are crucial for the movement of charged particles in living organisms. These channels act like tiny gates, controlling the flow of ions that generate vital electrical signals. The research team developed a technique using a miniature electrochemical reactor to create pores smaller than those found in nature, achieving dimensions close to just a few angstroms.
By leveraging the same principles that govern biological ion channels, researchers crafted solid-state versions capable of opening and closing at will. They utilized silicon nitride membranes to create a nanopore that served as a reaction chamber for generating even tinier pores. When they applied a negative voltage, it allowed controlled chemical reactions that altered the pore structure. This method demonstrated incredible repeatability, showcasing the controllable nature of their design. Such precision could pave the way for scientific progress in multiple sectors.
A Gateway to Innovation
The implications of this technology extend far beyond basic science. For instance, the ability to create ultrasmall pores opens the door for advanced DNA sequencing techniques. Scientists could potentially utilize these nanopores for single-molecule sensing, allowing for rapid and accurate genetic analysis. Moreover, the technology can facilitate neuromorphic computing, which aims to mimic the behavior of biological neurons. This form of computing could revolutionize artificial intelligence by enabling systems to process data in a more human-like manner.
Furthermore, by adjusting the chemical composition used in the reactions, researchers can fine-tune the size and behavior of nanopores. This adaptability makes it possible to analyze how ions transport through confined spaces, providing insights that could impact medical research, computational methods, and more. The pursuit of atom-sized gates represents a significant stride towards harnessing nature’s capabilities for technological advancement. As this research evolves, it may very well contribute to the next phase of human innovation.
Expand Your Tech Knowledge
Dive deeper into the world of Cryptocurrency and its impact on global finance.
Stay inspired by the vast knowledge available on Wikipedia.
TechV1