Summary Points
-
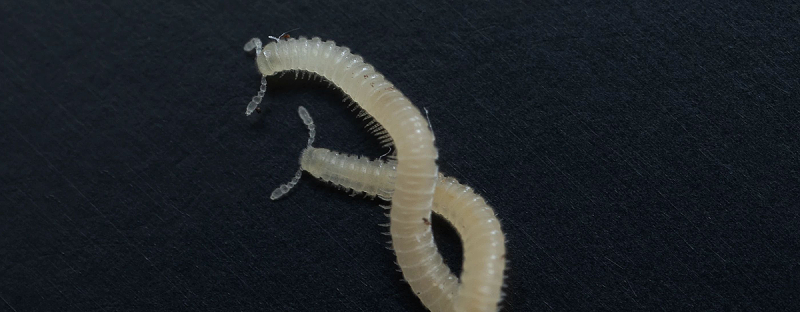
Researchers funded by the NSF discovered a new eyeless millipede species, Illacme socal, with nearly 500 legs thriving underground in Los Angeles, far from human sight.
-
This newly identified creature plays a vital ecological role by breaking down organic material and enriching the soil, supporting local biodiversity.
-
The millipede was found in Whiting Ranch Wilderness Park and possibly in Eaton Canyon Natural Area, highlighting the rich diversity that can exist even in urbanized regions.
- With millions of arthropod species yet to be described, the study underscores the importance of conservation efforts amid habitat loss in densely populated areas like Los Angeles.
A New Discovery Beneath Our Feet
Researchers have recently unveiled a remarkable find under the bustling streets of Los Angeles: a new species of millipede, named Illacme socal. This creature, pale and eyeless, possesses nearly 500 legs. Interestingly, it thrives underground, likely never surfacing to encounter the 18 million residents living above. While this may evoke images of a horror movie monster, it is worth noting that this millipede plays a vital role in the ecosystem. Millipedes help break down decaying matter. In turn, they release essential nutrients back into the soil, thus supporting new life in their environment.
Paul Marek and his team discovered this species in two locations: Whiting Ranch Wilderness Park and Eaton Canyon Natural Area. These areas, bursting with biodiversity, reveal that even in urban environments, significant biological discoveries await. Although only a few specimens of Illacme socal appeared, Marek suggests that similar species may reside elsewhere in Los Angeles. Urban development has likely diminished their habitats, amplifying the importance of conservation.
The Importance of Biodiversity
This discovery highlights a crucial aspect of our natural world: biodiversity. Currently, scientists estimate that Earth hosts between 4 million and 6 million arthropod species, yet only about 1 million have been documented. Marek’s work underscores the importance of identifying and cataloging these organisms, as each species contributes to a complex ecosystem. By understanding these underground communities, humanity can make better-informed decisions about conservation practices.
Furthermore, conserving species like Illacme socal aids in maintaining the delicate balance of our environment. Biodiversity supports not only wildlife but also human well-being. Healthy ecosystems provide clean air and water and contribute to food systems. As we progress in urban development, we must remember that the ground beneath us teems with life deserving protection. Research like Marek’s reminds us that even in densely populated areas, a wealth of diversity exists and merits our attention and respect.
Stay Ahead with the Latest Tech Trends
Stay informed on the revolutionary breakthroughs in Quantum Computing research.
Explore past and present digital transformations on the Internet Archive.
TechV1