Quick Takeaways
-
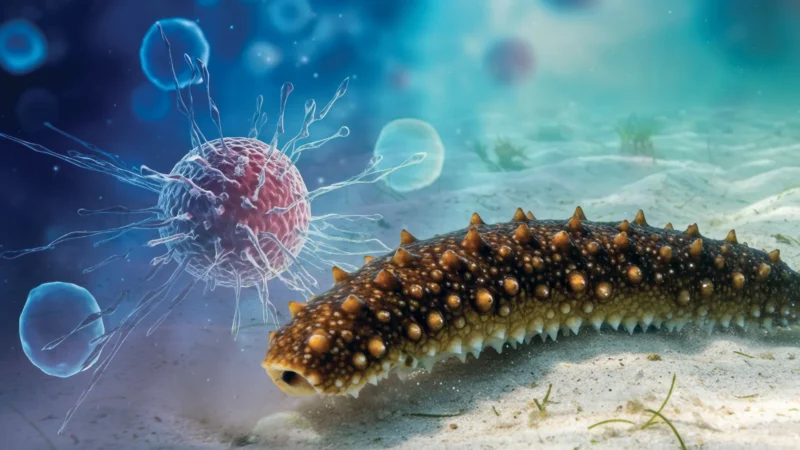
Cancer-Fighting Potential: Sea cucumbers produce a unique sugar compound that can block the cancer-promoting enzyme Sulf-2, potentially inhibiting cancer spread, according to a study by the University of Mississippi.
-
Unique Marine Compounds: The sugar in sea cucumbers, specifically fucosylated chondroitin sulfate, stands out due to its rare structure, making it a promising candidate for cancer research.
-
Safer Therapy Option: Unlike traditional cancer treatments, this marine compound does not interfere with blood clotting, reducing the risk of uncontrolled bleeding in patients.
- Research and Synthesis Challenges: While promising, harvesting from sea cucumbers poses logistical challenges; researchers aim to synthesize the compound chemically for future testing and therapeutic development.
Discovery of a Cancer-Fighting Sugar
Scientists recently unveiled a remarkable finding in sea cucumbers: a sugar compound that may help fight cancer. This compound, known as fucosylated chondroitin sulfate, effectively blocks an enzyme called Sulf-2, which plays a crucial role in cancer growth. Researchers at the University of Mississippi led the study, revealing how this marine invertebrate could contribute to medical breakthroughs. Sea cucumbers, often overlooked, serve as the ocean’s janitors, recycling nutrients and maintaining ecosystem health. Their unique chemical structures can provide insights seldom found in land animals.
Moreover, Sulf-2 modifies glycans, which are vital for cell communication and immune responses. When cancer alters these structures, it enables the disease to spread. The researchers demonstrated that inhibiting Sulf-2 could theoretically counteract this spread. This offers hope for developing new cancer therapies that are safer and more effective. Unlike existing treatments that can interfere with blood clotting, the sea cucumber compound does not carry this risk. As a result, it may pave the way for safer cancer treatment options.
Potential for Practical Applications
While the discovery is promising, practical challenges remain. Sea cucumbers are not abundant enough for large-scale drug production, presenting a significant hurdle. Researchers must find ways to synthesize this sugar compound for broader testing. The interdisciplinary collaboration behind this study highlights the importance of various scientific fields coming together to tackle complex health issues. By combining expertise in chemistry, biology, and pharmacology, they opened new avenues for cancer research.
If scientists succeed in developing a synthetic version of the sugar compound, we could witness a new chapter in cancer treatment. This innovation not only holds potential for improved patient outcomes but also illustrates a shift toward utilizing marine resources responsibly. As we continue to explore the ocean’s depths, we must remain hopeful that such discoveries will strengthen our fight against diseases like cancer and enhance our understanding of nature’s gifts.
Continue Your Tech Journey
Dive deeper into the world of Cryptocurrency and its impact on global finance.
Discover archived knowledge and digital history on the Internet Archive.
TechV1